What is Slag Inclusion in Lost Foam Casting
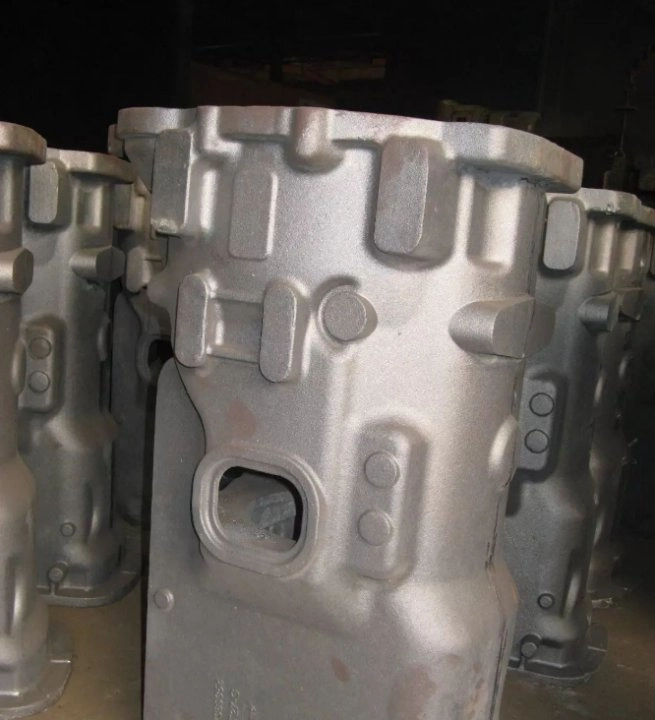
Slag inclusion is a defect where sand particles, coating fragments, and other impurities enter the casting along with molten metal during pouring. After machining, these defects appear as white or black-gray spots on the surface of the casting—white spots are quartz sand particles, while black-gray ones are slag, coating residue, and decomposition products of foam patterns. This defect is commonly referred to as “sand entrapment” or “slag inclusion.” It is prevalent in lost foam casting and difficult to eliminate completely. Only meticulous control at every stage can significantly reduce its occurrence and improve casting quality.
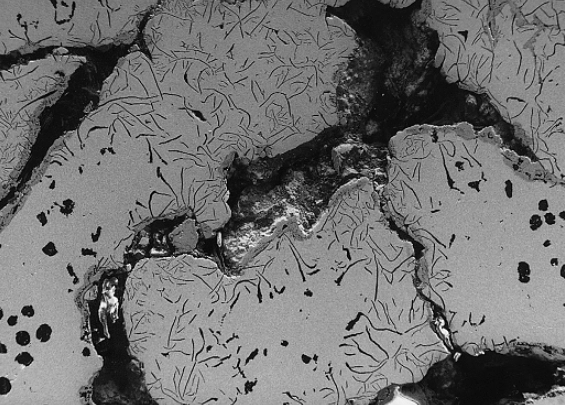
Causes of Slag Inclusion and Sand Entrapment
Issues in the Gating System and Foam Pattern Coating
All parts from the pouring cup to the gating system and into the casting cavity can contribute to slag inclusion, especially at joints between the gating system and casting body. The most critical causes include cracking or detachment of coating on foam patterns, particularly at junctions like straight sprue to runner or runner to ingate. If coatings fall off or crack, sand grains and debris can easily enter molten metal, forming inclusions.
Process Parameters (Pouring Head, Temperature, Vacuum, Sand Grain Size)
Process parameters such as pouring pressure head height, metal temperature, vacuum degree, and sand grain size also heavily influence slag inclusion formation. Incorrect parameter settings can cause excessive turbulence or erosion of coatings during pouring.
Handling and Transportation of Foam Patterns
Damage during transportation or improper handling of coated foam patterns can lead to cracks or detachment in the coating layer before pouring even begins. These defects become entry points for sand and impurities during pouring.
Methods and Measures to Reduce or Eliminate Slag Inclusion
Coating

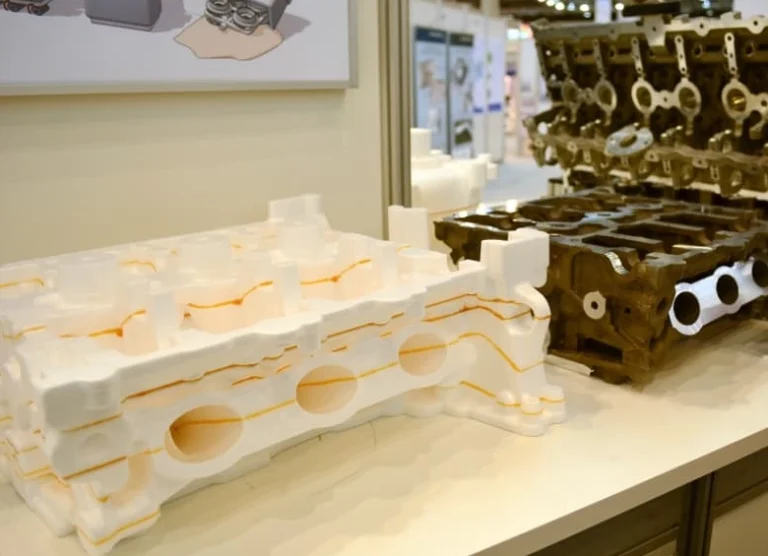
Lost foam casting coatings serve multiple purposes: improving surface finish; preventing sand adhesion; aiding de-sanding; allowing gases from decomposing foam to escape; preventing metal infiltration into sand mold; increasing pattern rigidity; and ultimately enhancing dimensional accuracy and yield rate. To prevent slag inclusion, coatings must have high strength—both at room temperature (to resist cracking during drying/transport) and high temperature (to withstand molten metal erosion). Coatings for gating systems should have higher refractory strength than those for castings themselves due to prolonged exposure to hot metal flow.
Mold Assembly and Packing
During mold assembly, no cracks or looseness should exist at joints like sprue-runner or runner-ingate connections. Ensure proper reinforcement using braces if needed. Place pattern assemblies gently on bottom sand without suspension. Avoid aggressive sand addition directly onto patterns—use soft hoses initially followed by rain-like sprinkling after vibration starts. Initial vibration should be gentle until patterns are buried in dry sand; then increase amplitude gradually. Never bend sprues during vibration as it risks cracking coatings. Before pouring, clean pouring cups thoroughly to remove dust or floating particles that could introduce inclusions.
Pouring Head, Temperature, and Time
Higher pressure heads increase turbulence and erosion risk—match ladle size appropriately with casting volume. Avoid using large ladles for small molds. Keep ladle nozzle close to pouring cup to reduce free-fall height of molten metal. For gray iron: tap temp ~1480°C; pour at 1380–1420°C. For ductile iron: tap above 1500°C; pour at 1420–1450°C. Steel castings: pour between 1480–1560°C. For 300–500 kg molds: aim for 10–20 seconds pour time per mold box.
Vacuum Control
Vacuum enhances dry sand compaction, gas evacuation, mold filling capability, and improves working conditions under sealed environments. However, excessive vacuum increases risk of drawing in impurities through cracks in coating layers. Recommended vacuum level for cast iron is 0.025–0.04 MPa.
Slag Traps and Riser Design
Incorporating slag traps within gating systems or placing risers designed specifically for slag collection helps isolate impurities from entering the final casting cavity effectively.
Mold Sand Quality
Sand grain size impacts both adhesion and inclusion defects—too coarse leads to more inclusions; too fine restricts permeability. For iron castings, use washed quartz sand with a grain size of 30/50 mesh for optimal results.
Molten Metal Purification
Molten metal purification is critical throughout melting through pouring stages in lost foam casting. Filtration techniques help remove non-metallic inclusions before they reach molds—this remains one of the key technologies ensuring clean castings in this process.
Conclusión
Reducing slag inclusion in lost foam casting requires holistic control across materials selection, equipment precision, process optimization, handling protocols, and real-time monitoring systems.
Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., Ltd provides advanced solutions specifically tailored for optimizing each step involved in lost foam production.
PREGUNTAS FRECUENTES
Q1: Why does coating quality matter so much?
Because cracked or detached coatings allow direct entry points for sand grains into molten metal flows—leading directly to slag inclusions that degrade surface quality post-machining.
Q2: What kind of vacuum system ensures consistent negative pressure?
The central vacuum unit adopts PLC automatic control The negative pressure pump adopts multiple sets of variable frequency control The negative pressure of the system is maintained at -0.5MPa to -0.8MPa
Q3: How does Hangzhou Ouchen ensure uniform heating during molding?
The exclusive design of the anti 7-shaped and all-round dispersion sequence steam drainage penetration heating method solves the problem of uniform heating temperature for large-sized disappearing template materials
Q4: How are beads matured properly before use?
Due to the negative pressure inside the newly prepared beads they need to be matured for a period of time usually 8-12 hours depending on ambient temperature
Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., Ltd – Leading Manufacturer of Lost Foam Casting Equipment
Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., LTD,is specialized in the production of high-end intelligent lost foam cast white area equipment enterprises The company introduces German EPS/EPP top technology combined with a number of independent intellectual property patents It has been innovative in science and technology research and development won the honor of “Science and technology small and medium-sized enterprises in Zhejiang Province”
From automatic pre-foaming machines with electromagnetic-steam hybrid heating methods that avoid “dead beads”, to vertical PLC hydraulic forming machines equipped with remote debugging features ensuring precise mold shaping—Ouchen’s solutions address every pain point associated with slag inclusion.
Their centralized vacuum system maintains consistent negative pressure levels while recovering heat energy efficiently without discharging wastewater—a sustainable solution aligned with modern industrial standards.
For foundries aiming for high-quality lost foam castings with minimal defects like slag inclusion or sand entrapment—Ouchen’s integrated systems offer a proven path forward backed by innovation-driven engineering excellence. Contáctenos hoy for the best deal.





