Lost-foam casting is a modern metal casting technique that merges innovation with practicality. It is widely utilized in industries requiring intricate, high-precision metal parts and continues to evolve thanks to advancements in automation and materials technology. Lost foam casting is as close as you can get to manufacturing “magic”—the way it can transform a delicate foam model into a solid metal item with almost unreal precision is practically sorcery.
What Is Lost-Foam Casting
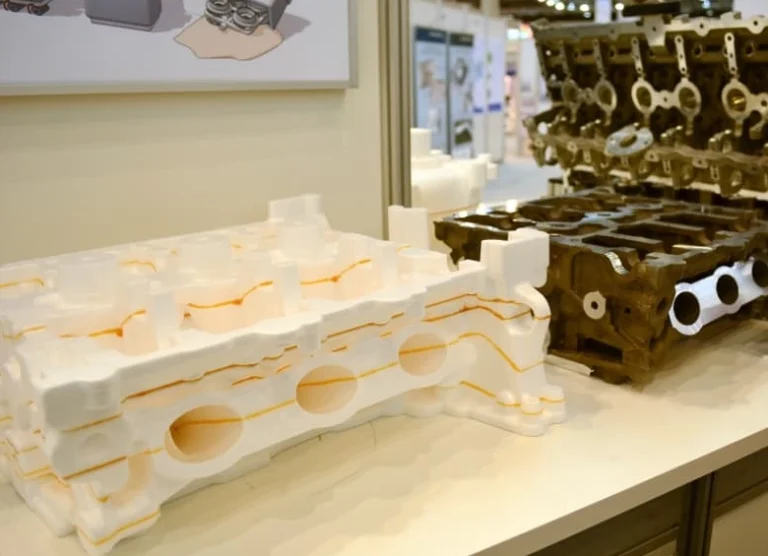
Also going by the names evaporative casting and the expanded polystyrene process, lost-foam casting is a technique that involves using expanded polystyrene foam as a mold that shapes molten metal and evaporates when it’s done. It came about in the late 1950s and is still a popular method today for both manufacturers and intrigued hobbyists. The pattern for the item you’re looking to make is cut from a foam block and coated in ceramic or another covering. This coating maintains separation between the foam and sand during the casting process. The method offers notable advantages including high dimensional accuracy and reduced need for secondary machining.
How It Works
First, the foam molds are prepared. These are in the shape of the intended finished product and they get filled through a gating system with passages that allow for precise design specs. Next, you bond the foam pattern or mold to the gating mechanism to make sure the alignment is spot on. Then you’ll apply dip paint, which, when dry, creates a ceramic coating on your mold, boosting its toughness, heat resistance, and ability to handle the high temperatures of the metal.
Once this is done, you’ll place the mold and gating mechanism (which are now one piece) into a bucket, container, or vessel of dry sand. After filling with sand, the container will go through vibration to make sure that the sand fully encompasses the module. This is when the molten metal gets poured into the mold. The heat of this makes the mold vaporize (sorcery!), leaving room for the metal to fill in and form. Finally, after the molds have cooled, they’ll go through cleaning and finishing. You can also recycle the sand.
Applications
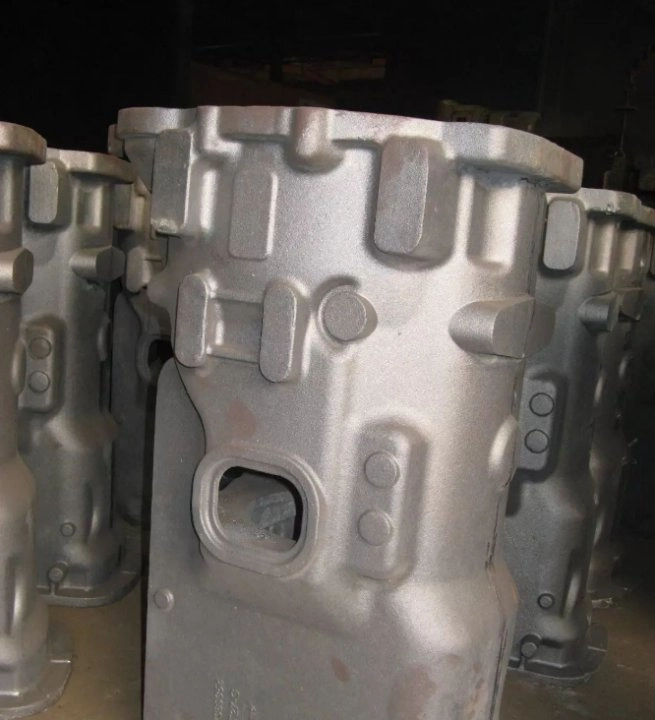
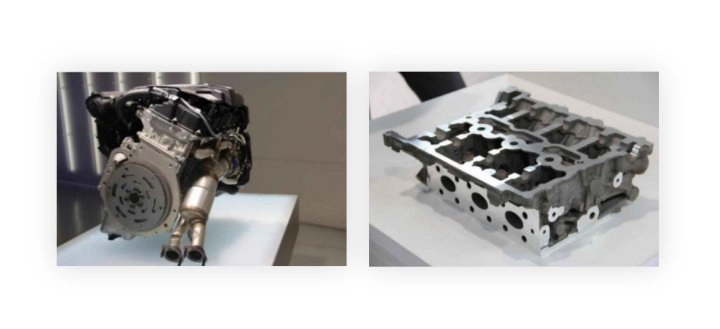
When you want an intricate or complex part with thinner walls or perhaps inner channels, you can look to lost-foam casting to get the job done. You’ll find the likes of cylinder heads, engine blocks, cooling system housings, and other engineered parts made in this way.
Lost-foam casting allows for the creation of highly complex, near-net-shape parts with intricate geometries that would be difficult or impossible to achieve using traditional casting methods, as the foam pattern eliminates the need for cores and parting lines. This advantage translates into real-world applications such as lightweight automotive engine components, intricate aerospace structures, and efficient pump housings, reducing machining costs and material waste while enabling innovative designs.
Materials and Metals Used
Steels and stainless steels: These alloys are popular for melting down and pouring into the mold because they’re strong and very resistant to corrosion. Stainless steel is usually a touch more expensive than other metals, but its positive characteristics often make it worth the price.
Aluminum alloys: These are often pretty affordable materials when used for lost-foam casting. Because they’re lightweight, strong, and thermally conductive, manufacturers and hobbyists often look to different aluminum alloys.
Cast irons: Whether gray or ductile, cast iron is strong and resistant to wear, making it a good choice for this manufacturing method. This is especially true for more heavy-duty situations.
Nickel alloys: Thanks to how well they can handle heat and corrosive environments, nickel alloys are another go-to choice for lost-foam casting. They can be more expensive
Sand: You’ll typically use dry sand to fill the container for lost-foam molding. Sometimes “green sand” is used
Lost-Foam Casting vs. Sand Casting
| Details | लॉस्ट-फोम कास्टिंग | सैंड कास्टिंग |
|---|---|---|
| प्रक्रिया | Molds are made from foam and coated, then vaporized | Molds are made of compacted sand |
| Complexity | Ideal for complex and intricate parts | Ideal for bigger |
| सतह खत्म | Smooth finish with precise dimensions | Rougher surface |
| Cost & Tooling | The upfront cost is higher | More cost-effective |
| Part Size & Weight | Can be used for small | Great for larger parts |
FAQs on Lost-Foam Casting
Can Copper Alloys Be Used as Casting Material for Lost-Foam Casting?
Yes. Although less common due to their high thermal conductivity affecting foam vaporization timing.
Are Lost-Foam Casting Products Heat Resistant?
Yes. Especially when using heat-resistant alloys like stainless steel or nickel-based materials.
Are Lost-Foam Casting Products High Quality?
Yes. The process allows near-net-shape production with minimal machining requirements.
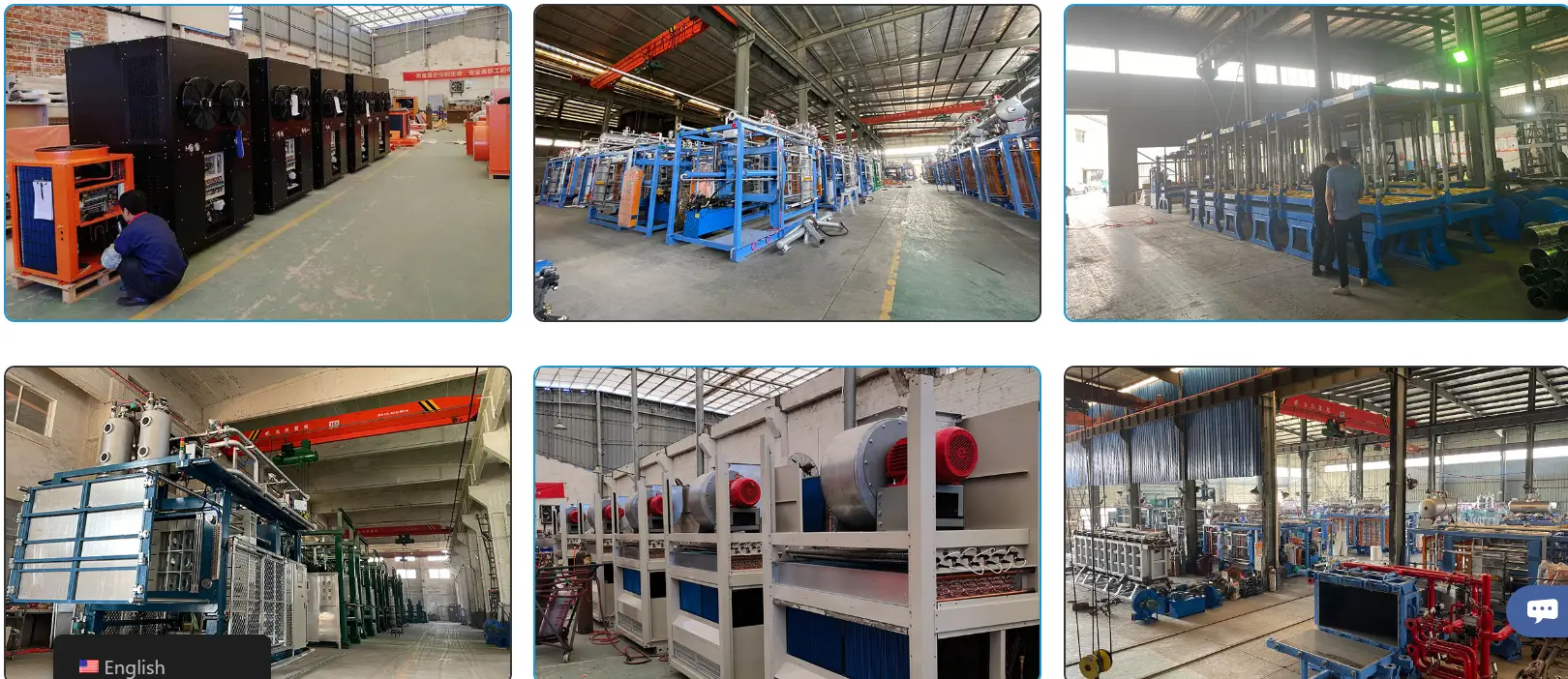

How Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., LTD Can Help
हांग्जो ओचेन टेक्नोलॉजी कं, लिमिटेड,is specialized in the production of high-end intelligent lost foam cast white area equipment enterprises focusing on automation research and high-end equipment manufacturing in this field.
The company introduces German EPS/EPP top technology combined with a number of independent intellectual property patents has been innovative in science and technology research and development
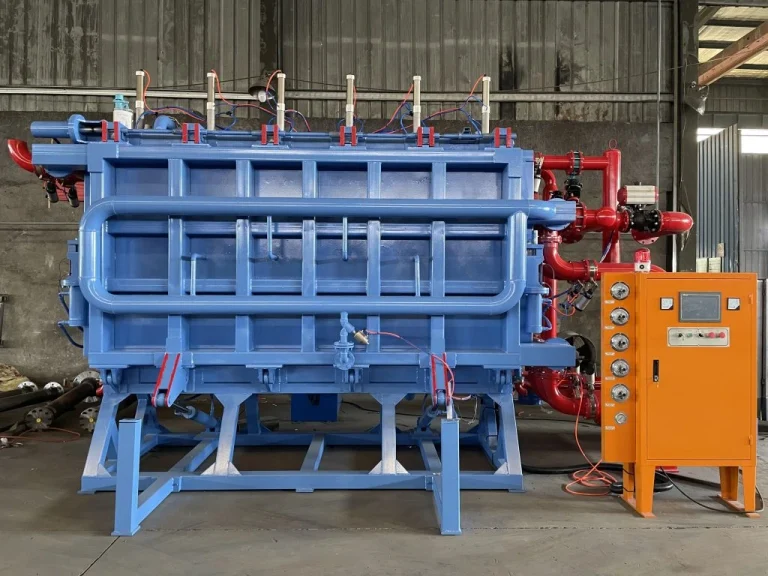
Their advanced equipment includes:
- Fully automatic pre-foaming machines using electromagnetic-steam hybrid heating systems
- Maturation silos that ensure optimal bead expansion force by balancing internal pressure
- Vertical PLC hydraulic forming machines with remote control capabilities
- Central vacuum systems featuring closed-loop air energy recovery technologies
- Lift type paint mixers offering anti-sedimentation immersion tanks made from stainless steel
These innovations support efficient production cycles (8–10 minutes per board), low deformation rates post-molding due to quick vacuum cooling. संपर्क हांग्जो ओचेन टेक्नोलॉजी कं, लिमिटेड for equipment ordering.





