Apa yang hilang buih
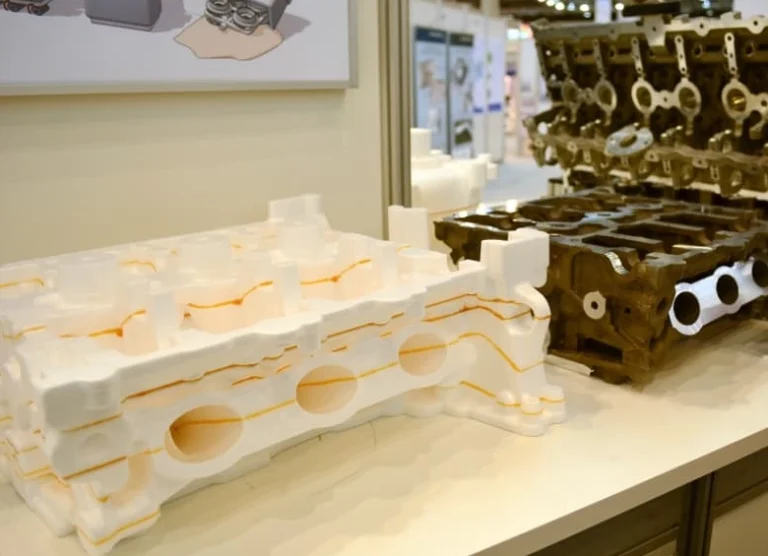
Lost Foam Casting is a neat way to make detailed metal parts. It uses a foam shape to form precise pieces. A polystyrene foam pattern gets coated with a heat-proof material. Then, it’s placed in loose sand. When hot metal is poured in, the foam burns away. This leaves a space that shapes the final metal part. This method skips traditional cores and parting lines. It allows fancy shapes and cuts down on extra machining.
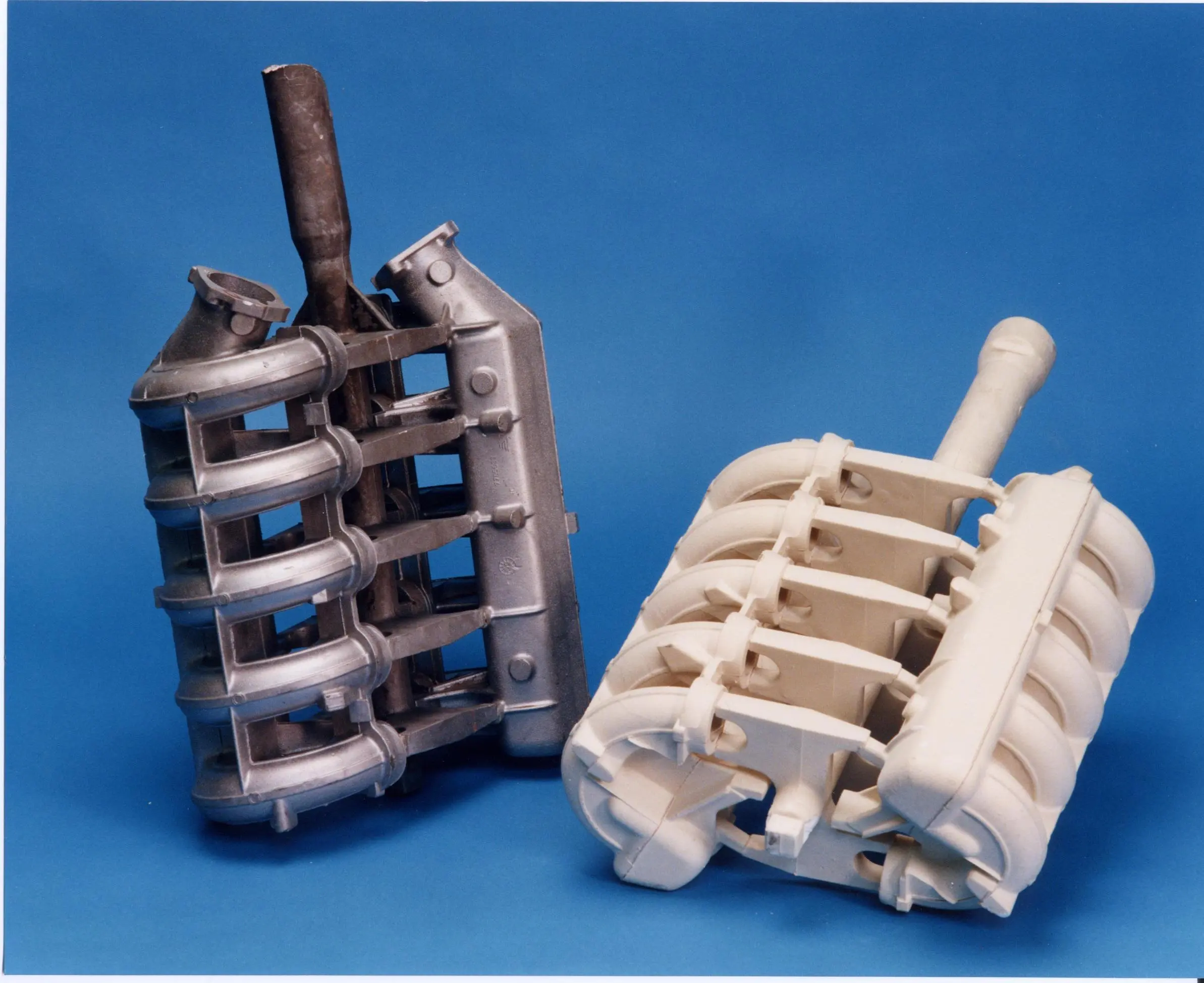
Preparing the Foam Pattern
Designing the Pattern for Accurate Mold Formation
Good lost foam casting starts with a spot-on foam design. The foam shape must match the final metal part exactly. Special computer programs, like CAD, help design these patterns. They account for size changes and angles. This keeps the part’s shape right during casting.
Cutting and Assembling the Foam Pattern
The foam pattern is usually made from expanded polystyrene (EPS). It can be cut with CNC machines, molded, or shaped by hand. For tricky shapes, several foam pieces are glued together with hot glue or joined with clips. A smooth assembly stops problems from bad fits or weak spots when pouring metal.

Coating and Drying the Foam Pattern
Purpose of Refractory Coating in Lost Foam Casting
A key step is putting a heat-proof coating on the foam shape. This coating shields the hot metal from the burning foam. It keeps the mold strong and the surface smooth. It also controls gas flow during pouring.
Applying Coating Evenly to Prevent Defects
To avoid flaws like rough spots or trapped bits, the coating must go on evenly. It can be dipped, brushed, or sprayed on. Some parts need extra layers based on their shape or heat load.
Proper Drying Techniques for Optimal Mold Performance
After coating, the foam shape needs to dry fully before going into sand. This stops steam from forming when metal is poured. Drying can happen in ovens or open air, depending on the job size. Bad drying can cause bubbles or holes in the casting.
Setting Up the Mold in the Flask
Selecting an Appropriate Flask Size and Shape
The flask holds the foam shape and loose sand. It must be big enough for the pattern and extra sand around it. A too-small flask can mess up sand packing or make the mold shaky.
Positioning the Pattern within the Flask
Placing the foam shape correctly helps metal flow smoothly. The gating system—sprues, runners, risers—is often built into the foam. This reduces mess and helps the metal harden evenly.
Filling with Unbonded Sand for Mold Stability
After setting the coated pattern in the flask, loose silica sand surrounds it. Unbonded sand flows easily around tricky shapes. It doesn’t need chemical glues because it packs tight with shaking.
Compacting and Ventilation Considerations
Vibrating the Sand to Ensure Uniform Compaction
Shaking the sand packs it tightly around the foam without breaking it. Even packing keeps the mold steady. This affects how accurate and smooth the final part is.
Managing Airflow and Gas Escape During Pouring
When hot metal burns the foam, gases form. These must escape through the coating and sand vents. Poor airflow can trap gases, causing holes inside the part. Good vent paths are a must for clean castings.
Melting and Pouring the Metal
Choosing Suitable Metals for Lost Foam Casting
Lost foam casting works with metals like gray iron, ductile iron, aluminum, and magnesium. The choice depends on needs like strength, weight, rust resistance, or heat handling.
Melting Techniques Based on Metal Type
Different metals need different melting methods. Induction furnaces work for steel and iron. Gas-fired pots are often used for aluminum. Keeping the right melt heat ensures smooth flow without extra damage.
Pouring Procedures for Accurate Mold Filling
Pouring needs to be steady and calm to avoid mess. This keeps the mold stable and stops flaws. Automated pouring systems keep things even across batches. Ceramic filters at entry points clean the metal better.
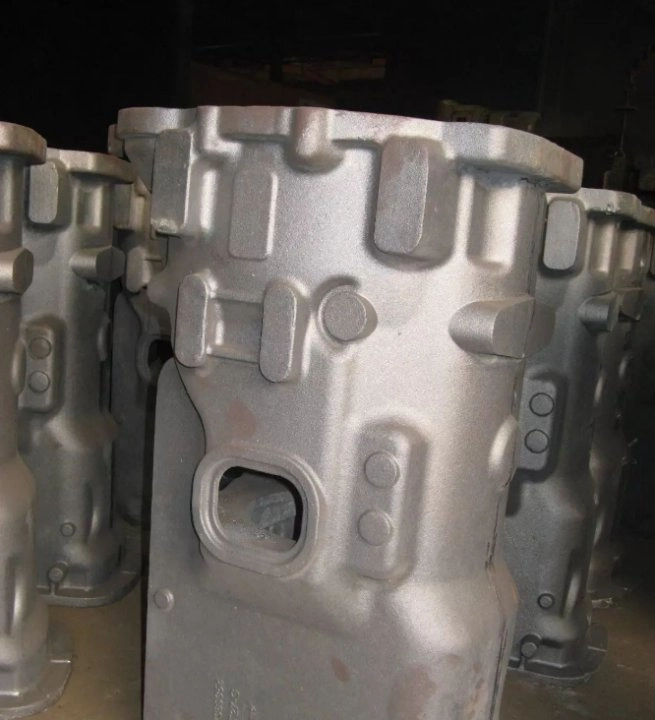
Cooling and Finishing the Casting
Allowing Adequate Cooling Time to Avoid Cracks or Warping
After pouring, castings need slow cooling in their sand molds. This prevents cracks or twists from quick temperature changes. Cooling time varies by metal type, part thickness, and air conditions.
Removing Sand and Cleaning Residual Material from Castings
Once cool enough, castings come out of flasks. Loose sand is shaken off. Blasting or washing removes leftover coating stuck on during casting.
Post-Casting Operations and Quality Control
Inspecting for Surface Defects or Internal Flaws
Looking closely spots surface issues. Special tests, like X-ray scans, find hidden flaws like holes or trapped bits from poor gas escape.
Machining or Heat Treating as Required
Some parts need machining for exact sizes. Heat treatments, like annealing or quenching, improve strength for specific uses.
Ensuring Dimensional Accuracy Against Original Design
Finished parts are checked with measuring tools against the original computer designs. This ensures they match the planned sizes exactly.
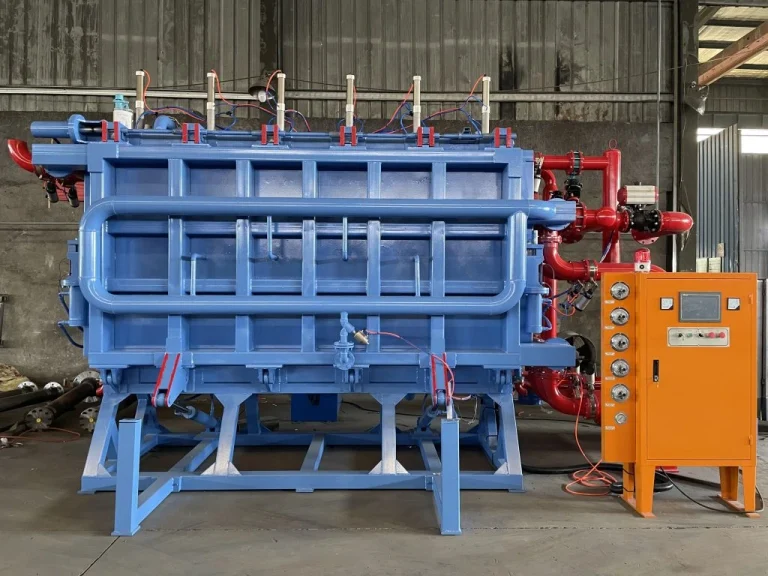
Choose Lost Foam Casting Foam Molding Machine from Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., LTD
For lost foam casting, picking reliable gear is key. Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., Ltd offers top-notch lost foam molding machines. They’re built for high-speed work. These machines make precise EPS patterns with steady density. This is vital for great final parts. They have automatic controls for cutting, shaping, gluing, and drying. These keep things even across big production runs.
Their machines fit smoothly into foundry work, whether making small aluminum parts or lots of ductile iron pieces. Choosing Hangzhou Ouchen’s tech means strong performance with expert support to improve lost foam casting results.
FAQ
What materials can be used in lost foam casting?
Lost foam casting works with metals like gray iron, ductile iron, and aluminum alloys.
Why use unbonded sand instead of bonded sand?
Unbonded silica sand flows well around tricky shapes. It doesn’t need chemical glues since it packs tight with shaking.
How does lost foam casting reduce machining needs?
Lost foam casting makes parts close to final shape. It copies detailed EPS patterns without traditional cores or parting lines.
What causes porosity in lost foam castings?
Porosity happens when gases from burning EPS can’t escape well. This is due to poor vents in coatings or sand molds.
Is automation possible with this process?
Yes. Modern foundries use automated systems, like robotic pouring arms and CNC molding machines from Hangzhou Ouchen Technology Co., LTD. These boost consistency and cut labor costs.





